Membership Options
WEEKLY CLASSES from
just £4.95/hour
We’ve designed all of our lessons to offer unrivalled quality and service. Read on to find out about our membership options.
Has your child lost confidence in Maths, English or Science?
Do you feel like the work they're doing at school is just too simple and you know they're capable of learning so much more?
We’ve taught 1000’s of students since we started teaching in 2007 and over the years we’ve adapted all of our content to ensure that no child gets left behind. Our lessons are designed to help KS2, KS3 and KS4 students cover all the key syllabus material in Maths, English Language, Biology, Chemistry and Physics at a speed that they can learn effectively, retain information, and build on their subject knowledge.
Whether you’re the parent of a child who struggles with Maths, English or Science or just a parent wanting your child to achieve the best possible results in the SATs or GCSE exams, you’ll be pleased to know that our classes are offered in 3 tiered membership plans that offer support at varying levels to meet the needs of your child!

We pride our lessons on being 100% interactive with our teachers.

Our lesson are affordable with prices starting from just £4.95

Key to students succeeding is regular weekly homework

RATED EXCELLENT
BY PARENTS & STUDENTS ACROSS THE UK
OUTSTANDING RESULTS **2023**
- 100% of A-level students achieved their minimum target grade
- 98% of A-level students who studied with us for at least 6 months achieved A*-B in the subjects we tutored them in
- 40% of A-level students tutored received offers from Oxbridge
- 96% of GCSE students sitting a higher paper achieved a level 7-9 in Math, English and Science
- 93% of GCSE students achieved at least 1 grade higher than their predicted score in Math, English and Science after attending our classes
- 100% of students surveyed before exams felt more confident after attending our classes for 3 months or more before their exams
- 100% of students sitting exam papers this year said they were grateful for the work The Academy did to prepare them for these life changing exams!
our lessons
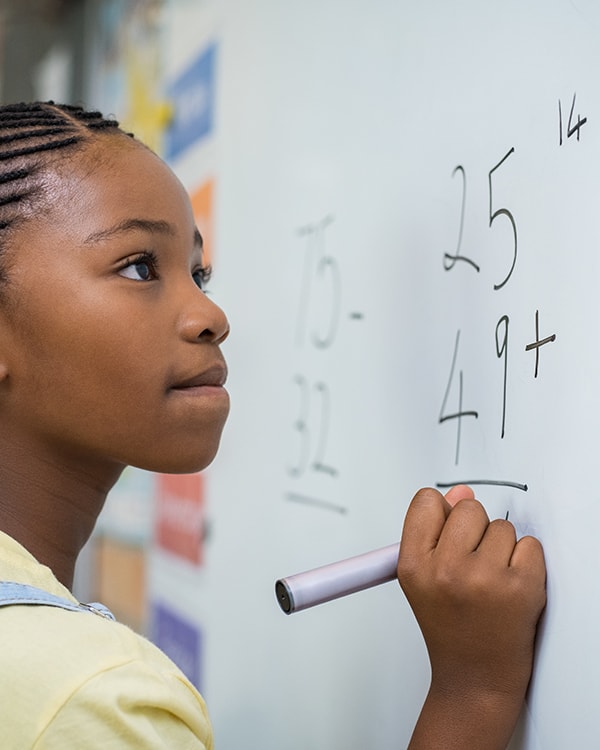
Our experience has shown the only sure way to achieve the best results in the SATs or GCSE exams is by ensuring a consistent learning plan and regular teaching that breaks concepts into easy to digest chunks!
Our lessons are all delivered through our 3-step success methodology that ensures: material is taught well with step by step guidance, practiced and then reviewed for corrections and model answers.
Membership options
Our lessons are offered in 3 types of membership plans that offer varying support. We’ve outlined the differences between all our membership plans below.
Silver
membership
Our most basic membership plan offers unrivalled value.
Each lesson includes:
Choose from Maths, English Language, Biology, Chemistry & Physics
4 hours per subject every month
60 mins per class
Email support
Material in line with national curriculum
Platinum
Membership
Ideal for students wanting ongoing revision and practice. Includes everything in our Silver Membership plus:
Free revision tools and study material
Termly exams and weekly assessments
Students able to ask questions in lesson
Homework supplied
Comprehensive revision notes
Platinum+
membership
Recommended for parents wanting comprehensive support. Includes everything in Platinum Membership plus:
5 hours per subject every month
1-1 help in class
Personalised feedback and termly reporting
Telephone support
Lesson recordings

We've taught over 5000 students.

All our teaching material is in line with the national curriculum

Students join 1 weekly class every week
OUR MOST POPULAR PACKAGES
Our charges are based on the membership selected and the weekly classes you subscribe to. With all membership plans, we offer a discount to parents when they opt in for more weekly lessons. We’ve shared some of popular plans below:
-
Silver Membership (3 subjects a week) £65/month
Choose from: Maths, English Language, Biology, Chemistry & Physics
-
Silver Membership (5 subjects a week) £129/month
Choose from: Maths, English Language, Biology, Chemistry & Physics
-
Platinum membership (3 subjects a week) £169/month
Choose from: Maths, English Language, Bio-Chemistry & Physics
-
Platinum membership (5 subjects a week) £199/month
Choose from: Maths, English Language, Bio-Chemistry & Physics
-
Platinum Plus Membership (2 subjects a week) £159/month
Choose from: Maths, English Language, Bio-Chemistry & Physics
-
Platinum Plus Membership (5 subjects a week) £299/month
Choose from: Maths, English Language, Bio-Chemistry & Physics
programme of study
All subjects taught will be broken down into themes and aims that cover requirements laid out in the national curriculum. Parents are free to select any level of class for their child. This means students who have fallen behind can cement ideas and concepts from the previous year, whilst those wanting to work ahead of class can learn material at least 1 year in advance. We’ve shared an example of our Maths, English and Biology programme below.
Term 1
| Statistics | Interpret and present data using bar charts, pictograms and tables. |
| Statistics | Solve one-step and two-step questions using information presented in tables. |
| Addition and subtraction | Add and subtract numbers mentally. |
| Addition and subtraction | Solve problems, including missing number problems, using number facts, place value, and more complex addition and subtraction. |
| Geometry – properties of shapes | Identify right angles, recognise that two right angles make a half-turn, three make three quarters of a turn and four a complete turn; Identify whether angles are greater than or less than a right angle. Recognise angles as a property of shape or a description of a turn. |
| Multiplication and division | Solve problems, including missing number problems, involving multiplication and division, including positive integer scaling problems and correspondence problems in which n objects are connected to m objects. |
| Fractions | Recognise and show, using diagrams, equivalent fractions with small denominators. |
| Fractions | Count up and down in tenths; recognise that tenths arise from dividing an object into 10 equal parts and in dividing one-digit numbers or quantities by 10. |
| Fractions | Recognise, find and write fractions of a discrete set of objects: unit fractions and non-unit fractions with small denominators. |
| Geometry – properties of shapes | Identify horizontal and vertical lines and pairs of perpendicular and parallel lines. |
| Fractions | Recognise, find and write fractions of a discrete set of objects: unit fractions and non-unit fractions with small denominators. |
| Fractions | Add and subtract fractions with the same denominator within one whole. |
| Fractions | Compare and order unit fractions, and fractions with the same denominators. |
Term 2
| Number | Recognise the place value of each digit in a three-digit number. |
| Number | Recognise the place value of each digit in a three-digit number. |
| Number | Compare and order numbers up to 1000. |
| Number | Compare and order numbers up to 1000. |
| Geometry | Draw 2D shapes. |
| Geometry | Recognise 3D shapes in different orientations and describe them. |
| Geometry | Recognise 3D shapes in different orientations and describe them. |
| Geometry | Recognise 3D shapes in different orientations and describe them. |
| Measurement | Measure and compare: lengths; mass; volume/capacity. |
| Geometry | Describe positions on a 2D grid as coordinates in the first quadrant; Describe movements between positions as translations of a given unit to the left/right and up/down. |
| Measurement | Add and subtract: lengths; mass; volume/capacity. |
| Measurement | Measure the perimeter of simple 2-D shapes. |
| Measurement | Add and subtract amounts of money to give change, using p in practical contexts. |
Term 1
| Multiplication and division | Multiply two-digit and three-digit numbers by a one-digit number using formal written layout. |
| Multiplication and division | Use place value, known and derived facts to multiply and divide mentally, including: multiplying by 0 and 1; dividing by 1; multiplying together three numbers. |
| Multiplication and division | Recognise and use factor pairs and commutativity in mental calculations. |
| Multiplication and division | Pupils practise to become fluent in the formal written method of short multiplication and short division with exact answers (non statutory). |
| Addition and subtraction | Add and subtract numbers with up to 4 digits using the formal written methods of columnar addition and subtraction where appropriate. |
| Addition and subtraction | Estimate and use inverse operations to check answers to a calculation. |
| Addition and subtraction | Practise mental methods with increasingly large numbers to aid fluency (non-statutory). |
| Addition and subtraction | Solve addition and subtraction two-step problems in contexts, deciding which operations and methods to use and why. |
| Fractions | Recognise and write decimal equivalents of any number of tenths or hundredths. |
| Measurement | Read, write and convert time between analogue and digital 12- and 24-hour clocks. |
| Fractions | Find the effect of dividing a one- or two-digit number by 10 and 100, identifying the value of the digits in the answer as ones, tenths and hundredths. |
| Fractions | Round decimals with one decimal place to the nearest whole number. |
| Fractions | Solve simple measure and money problems involving fractions and decimals to two decimal places. |
Term 2
| Statistics | Interpret discrete data using bar charts. |
| Statistics | Present discrete data using bar charts. |
| Statistics | Interpret continuous data using time graphs. |
| Statistics | Present continuous data using time graphs. |
| Fractions | Recognise and write decimal equivalents to 1/4, 1/2, 3/4; Recognise and write decimal equivalents of any number of tenths of hundredths. |
| Fractions | Recognise and write decimal equivalents of any number of tenths or hundredths. |
| Fractions | Add and subtract fractions with the same denominator. |
| Fractions | Recognise and show, using diagrams, families of common equivalent fractions |
| Geometry | Describe positions on a 2D grid as coordinates in the first quadrant. |
| Geometry | Identify, describe and represent the position of a shape following a reflection, using the appropriate language, and know that the shape has not changed. |
| Geometry | Describe movements between positions as translations of a given unit to the left/right and up/down. |
| Geometry | Plot specified points and draw sides to complete a given polygon. |
| Geometry | Plot specified points and draw sides to complete a given polygon. |
Term 1
| Addition and subtraction | Add and subtract whole numbers with more than 4 digits, including using formal written methods. |
| Addition and subtraction | Solve addition and subtraction in contexts, deciding which operations and methods to use and why. |
| Addition and subtraction | Add and subtract numbers mentally with increasingly large numbers and use rounding to check answers to calculations and determine, in the context of a problem, levels of accuracy. |
| Multiplication and division | Identify multiplies and factors, including finding all factor pairs of a number, and common factors of two numbers. |
| Multiplication and division | Divide numbers up to 4 digits by a one-digit number using the formal written method of short division and interpret remainders appropriately for the context. |
| Multiplication and division | Multiply numbers up to 4 digits by a one- or two-digit number using a formal written method, including long multiplication for two-digit numbers. |
| Multiplication and division | Recognise and use square numbers and cube numbers, and the notation for squared and cubed. |
| Fractions | Recognise mixed numbers and improper fractions and convert from one form to the other and write mathematical statements > 1 as a mixed number. |
| Fractions | Identify, name and write equivalent fractions of a given fraction, represented visually, including tenths and hundredths. |
| Geometry – position and direction | Identify, describe and represent the position of a shape following a reflection or translation, using the appropriate language, and know that the shape has not changed. |
| Fractions | Read, write, order and compare numbers with up to three decimal places. |
| Fractions | Read and write decimal numbers as fractions. |
| Fractions | Recognise the per cent symbol and understand that per cent relates to ‘number of parts per hundred’, and write percentages as a fraction with denominator 100, and as a decimal. |
Term 2
| Number | Count forwards or backwards in steps of powers of 10 for any given number up to 1 000 000 |
| Number | Round any number up to 1 000 000 to the nearest 10, 100 and 1000 |
| Number | Round any number up to 1 000 000 to the nearest 10 000 and 100 000 |
| Number | Count forwards and backwards with positive and negative whole numbers, including through zero. |
| Measurement | Convert between different units of metric measure. |
| Measurement | Convert between different units of metric measure. |
| Measurement | Understand and use approximate equivalences between metric units and common imperial units such as inches, pounds and pints. |
| Measurement | Understand and use approximate equivalences between metric units and common imperial units such as inches, pounds and pints. |
| Statistics | Solve comparison, sum and difference problems using information presented in a line graph. |
| Geometry | Identify 3D shapes, including cubes and other cuboids, from 2D representations & Distinguish between regular and irregular polygons based on reasoning about equal sides and angles. |
| Statistics | Solve comparison, sum and difference problems using information presented in a line graph. |
| Statistics | Complete, read and interpret information in tables, including timetables. |
| Statistics | Complete, read and interpret information in tables, including timetables. |
Term 1
| Fractions | Use common factors to simplify fractions; use common multiples to express fractions in the same denomination. |
| Fractions | Multiply simple pairs of proper fractions, writing the answer in its simplest form. |
| Fractions | Divide proper fractions by whole numbers. |
| Fractions | Multiply one-digit numbers with up to two decimal places by whole numbers. |
| Algebra | Express missing number problems algebraically. |
| Algebra | Enumerate possibilities of combinations of two variables. |
| Algebra | Find pairs of numbers that satisfy an equation with two unknowns. |
| Fractions | Associate a fraction with division and calculate decimal fraction equivalents for a simple fraction |
| Statistics | Interpret and construct pie charts and use these to solve problems. |
| Statistics | Calculate and interpret the mean as an average. |
| Fractions | Identify the value of each digit in numbers given to three decimal places and multiply and divide numbers by 10, 100 and 1000 giving answers up to three decimal places. |
| Measurement | Convert between miles and kilometres. |
| Measurement | Calculate the area of parallelograms and triangles. |
Term 2
| Number | Round any whole number to a required degree of accuracy. |
| Number | Round any whole number to a required degree of accuracy. |
| Number | Use negative numbers in context, and calculate intervals across zero. |
| Number | Use negative numbers in context, and calculate intervals across zero. |
| Geometry | Recognise, describe and build simple 3D shapes, including making nets. |
| Geometry | Recognise, describe and build simple 3D shapes, including making nets. |
| Geometry | Compare and classify geometric shapes based on their properties and sizes and find unknown angles in any triangles and quadrilaterals. |
| Geometry | Compare and classify geometric shapes based on their properties and sizes and find unknown angles in any regular polygons. |
| Ratio and Proportion | Solve problems involving similar shapes where the scale factor is known or can be found. |
| Algebra | Use simple formulae & Generate and describe linear number sequences. |
| Ratio and Proportion | Solve problems involving unequal sharing and grouping using knowledge of fractions and multiples. |
| Ratio and Proportion | Solve problems involving unequal sharing and grouping using knowledge of fractions and multiples. |
| Ratio and Proportion | Solve problems involving the relative sizes of two quantities where missing values can be found by using integer multiplication and division facts. |
Term 1
| Theme | Topic | Required Learning Objective |
| Geometry and measures | Geometry problems foundation | Apply the properties of angles at a point, angles at a point on a straight line, vertically opposite angles. |
| Statistics | Line graphs | Construct and interpret appropriate tables, charts, and diagrams, including frequency tables, bar charts, pie charts, and pictograms for categorical data, and vertical line (or bar) charts for ungrouped and grouped numerical data. |
| Number | Types of numbers | Use the concepts and vocabulary of prime numbers, factors (or divisors), multiples, common factors, common multiples, highest common factor, lowest common multiple, prime factorisation, including using product notation and the unique factorisation property |
| Geometry and measures | Area under a graph | Calculate and solve problems involving: perimeters of 2D shapes (including circles), areas of circles and composite shapes |
| Geometry and measures | Areas of shapes | Calculate and solve problems involving: perimeters of 2D shapes (including circles), areas of circles and composite shapes |
| Ratio, proportion and rates of change | Best buys | Use compound units such as speed, unit pricing and density to solve problems. |
| Geometry and measures | Circles | Calculate and solve problems involving: perimeters of 2D shapes (including circles), areas of circles and composite shapes |
| Ratio, proportion and rates of change | Conversion graphs | Change freely between standard units (for example, time, length, area, volume/ capacity, mass). |
| Ratio, proportion and rates of change | Conversions | Change freely between standard units (for example, time, length, area, volume/ capacity, mass). |
| Algebra | Coordinates and midpoints | Work with coordinates in all four quadrants. |
| Geometry and measures | Corresponding angles and alternate angles | Understand and use the relationship between parallel lines and alternate and corresponding angles. |
| Statistics | Data sampling and questionnaires | Construct and interpret appropriate tables, charts, and diagrams, including frequency tables, bar charts, pie charts, and pictograms for categorical data, and vertical line (or bar) charts for ungrouped and grouped numerical data. |
| Ratio, proportion and rates of change | Density mass volume | Use compound units such as speed, unit pricing and density to solve problems. |
Term 2
| Theme | Topic | Required Learning Objective |
| Algebra | Collecting like terms | Simplify and manipulate algebraic expressions to maintain equivalence by collecting like terms. |
| Algebra | Expanding single brackets | Simplify and manipulate algebraic expressions to maintain equivalence by multiplying a single term over a bracket. |
| Number | Fractions, decimals and percentages | Interpret percentages and percentage changes as a fraction or a decimal. |
| Ratio and proportion | Maps and scale drawings | Use scale factors, scale diagrams and maps. |
| Number | Percentage of amount & percentage change | Compare two quantities using percentages, and work with percentages greater than 100%. |
| Statistics | Pictographs | Construct and interpret appropriate tables, charts, and diagrams, including frequency tables, bar charts, pie charts, and pictograms for categorical data. |
| Probability | Probability basics & listing outcomes | Record, describe and analyse the frequency of outcomes of simple probability experiments involving randomness, fairness, equally and unequally likely outcomes, using appropriate language and the 0-1 probability scale. |
| Geometry | Projections, plans and elevations | Draw and measure line segments and angles in geometric figures, including interpreting scale drawings. |
| Statistics | Scatter graphs | Describe simple mathematical relationships between two variables (bivariate data) in observational and experimental contexts and illustrate using scatter graphs. |
| Algebra | Solving equations | Use algebraic methods to solve linear equations in one variable (including all forms that require rearrangement). |
| Statistics | Stem and leaf diagrams | Construct and interpret appropriate tables, charts, and diagrams. |
| Geometry | Symmetry | Describe, sketch and draw using conventional terms and notations: points, lines, parallel lines, perpendicular lines, right angles, regular polygons, and other polygons that are reflectively and rotationally symmetric. |
| Statistics | Types of data | Describe, interpret and compare observed distributions of a single variable through: appropriate graphical representation involving discrete, continuous and grouped data; and appropriate measures of central tendency (mean, mode, median) and spread (range, consideration of outliers). |
Term 1
| Theme | Topic | Required Learning Objective |
| Probability | Relative frequency | Understand that the probabilities of all possible outcomes sum to 1. |
| Ratio, proportion and rates of change | Reverse percentages | Solve problems involving percentage change, including: percentage increase, decrease and original value problems and simple interest in financial mathematics. |
| Algebra | Sequences and nth term | Recognise arithmetic sequences and find the nth term. |
| Geometry and measures | Similar shapes (foundation) | Identify and construct congruent triangles, and construct similar shapes by enlargement, with and without coordinate grids. |
| Algebra | Simultaneous equations (linear) | Use linear and quadratic graphs to estimate the values of y for given values of x and vice versa and to find approximate solutions of simultaneous linear equations. |
| Algebra | Solving inequalities | Understand and use the concepts and vocabulary of expressions, equations, inequalities, terms and factors. |
| Number | Standard form | Interpret and compare numbers in standard form A × 10^n (1 ≤ A < 10), where n is a positive or negative integer or zero. |
| Geometry and measures | Surface area of 3D shapes | Use the properties of faces, surfaces, edges and vertices of cubes, cuboids, prisms, cylinders, pyramids, cones and spheres to solve problems in 3D. |
| Geometry and measures | The four transformations | Identify properties of, and describe the results of, translations, rotations and reflections applied to given figures. |
| Ratio, proportion and rates of change | Unit conversions | Change freely between standard units (for example, time, length, area, volume/ capacity, mass). |
| Geometry and measures | Volume of 3D shapes | Use the properties of faces, surfaces, edges and vertices of cubes, cuboids, prisms, cylinders, pyramids, cones and spheres to solve problems in 3D. |
| Algebra | y = mx + c | Reduce a given linear equation in two variables to the standard form y = mx + c; calculate and interpret gradients and intercepts of graphs of such linear equations numerically, graphically and algebraically. |
| Algebra | Coordinates and ratios | Work with coordinates in all four quadrants. |
Term 1
| Theme | Topic | Required Learning Objective |
| Algebra | Functions (composite and inverse) | Recognise, sketch and produce graphs of linear and quadratic functions of one variable with appropriate scaling, using equations in x and y and the Cartesian plane. |
| Geometry and measures | Negative enlargements | Identify properties of, and describe the results of, translations, rotations and reflections applied to given figures. |
| Algebra | Proof higher | Model situations or procedures by translating them into algebraic expressions or formulae and by using graphs. |
| Ratio, proportion and rates of change | Ratios higher | Express one quantity as a fraction of another, where the fraction is less than 1 and greater than 1. |
| Geometry and measures | Similar shapes (area and volume) | Identify and construct congruent triangles, and construct similar shapes by enlargement, with and without coordinate grids. |
| Algebra | Simultaneous equations (non-linear) | Use linear and quadratic graphs to estimate the values of y for given values of x and vice versa and to find approximate solutions of simultaneous linear equations. |
| Algebra | Solve quadratics by factorisation | Simplify and manipulate algebraic expressions to maintain equivalence by: taking out common factors. |
| Ratio, proportion and rates of change | Best buys | Solve problems involving percentage change, including: percentage increase, decrease and original value problems and simple interest in financial mathematics. |
| Geometry and measures | Column vectors | Identify properties of, and describe the results of, translations, rotations and reflections applied to given figures. |
| Algebra | Gradients of real life graphs | Reduce a given linear equation in two variables to the standard form y = mx + c; calculate and interpret gradients and intercepts of graphs of such linear equations numerically, graphically and algebraically. |
| Number | Estimating | Use approximation through rounding to estimate answers and calculate possible resulting errors expressed using inequality notation a < x ≤ b. |
| Statistics | Grouped frequency tables | Construct and interpret appropriate tables, charts, and diagrams, including frequency tables, bar charts, pie charts, and pictograms for categorical data, and vertical line (or bar) charts for ungrouped and grouped numerical data. |
| Algebra | Powers and roots | Substitute numerical values into formulae and expressions, including scientific formulae. |
Term 1
| Theme | Topic | Required Learning Objective |
| Geometry and measures | Geometry problems foundation | Calculate surface areas and volumes of spheres, pyramids, cones and composite solids. |
| Algebra | Solving equations | Simplify and manipulate algebraic expressions (including those involving surds {and algebraic fractions}. |
| Algebra | Collecting like terms | Simplify and manipulate algebraic expressions (including those involving surds {and algebraic fractions}. |
| Algebra | Factorising | Simplify and manipulate algebraic expressions (including those involving surds {and algebraic fractions} by: factorising quadratic expressionsof the form x^2 + bx + c, including the difference of two squares; {factorising quadratic expressions of the form ax^2 + bx +c}. |
| Geometry and measures | Maps and scale drawings | Construct and interpret plans and elevations of 3D shapes. |
| Ratio, proportion and rates of changes | Percentage of amount & percentage change | Set up, solve and interpret the answers in growth and decay problems, including compound interest {and work with general iterative processes}. |
| Probability | Probability basics & listing outcomes | Use a probability model to predict the outcomes of future experiments; understand that empirical unbiased samples tend towards theoretical probability distributions, with increasing sample size. |
| Statistics | Types of data | Apply statistics to describe a population. |
| Algebra | Expanding single brackets | Simplify and manipulate algebraic expressions (including those involving surds {and algebraic fractions}. |
| Number | Fractions, decimals and percentages | Change recurring decimals into their corresponding fractions and vice versa. |
| Geometry and measures | Projections, plans and elevations | Construct and interpret plans and elevations of 3D shapes. |
| Statistics | Scatter graphs | Use and interpret scatter graphs of bivariate data; recognise correlation and know that it does not indicate causation; draw estimated lines of best fit; make predictions; interpolate and extrapolate apparent trends whilst knowing the dangers of so doing. |
| Statistics | Stem and leaf diagrams | Construct and interpret diagrams for grouped discrete data and continuous data, i.e. histograms with equal and unequal class intervals and cumulative frequency graphs, and know their appropriate use. |
Term 1
| Theme | Topic | Required Learning Objective |
| Algebra | Perpendicular lines | Use the form y mx c = + to identify parallel {and perpendicular} lines; find the equation of the line through two given points, or through one point with a given gradient. |
| Probability | Probability and tree diagrams (higher) | Calculate the probability of independent and dependent combined events, including using tree diagrams and other representations, and know the underlying assumptions. |
| Probability | Venn diagram (higher) | Calculate and interpret conditional probabilities through representation using expected frequencies with two-way tables, tree diagrams and Venn diagrams. |
| Statistics | Box plots | Interpret, analyse and compare the distributions of data sets from univariate empirical distributions through: appropriate graphical representation involving discrete, continuous and grouped data, {including box plots}. |
| Geometry and measures | Circle sector, segments and arcs | Calculate arc lengths, angles and areas of sectors of circles. |
| Ratio, proportion and rates of change | Ratios foundation | Compare lengths, areas and volumes using ratio notation and/or scale factors. |
| Algebra | Gradients of straight line graphs | Use the form y mx c = + to identify parallel {and perpendicular} lines; find the equation of the line through two given points, or through one point with a given gradient. |
| Statistics | Frequency tables | Construct and interpret diagrams for grouped discrete data and continuous data, i.e. histograms with equal and unequal class intervals and cumulative frequency graphs, and know their appropriate use. |
| Geometry and measures | Areas of shapes | Calculate surface areas and volumes of spheres, pyramids, cones and composite solids. |
| Number | Prime factors LCM HCF | Apply systematic listing strategies, {including use of the product rule for counting}. |
| Algebra | Simultaneous equations (linear) | Solve two simultaneous equations in two variables (linear/linear {or linear/quadratic}) algebraically; find approximate solutions using a graph. |
| Geometry and measures | Similar shapes (foundation) | Apply the concepts of congruence and similarity, including the relationships between lengths, {areas and volumes} in similar figures. |
| Algebra | Proof foundation | Know the difference between an equation and an identity; argue mathematically to show algebraic expressions are equivalent, and use algebra to support and construct arguments {and proofs}. |
Term 1
| Theme | Topic | Required Learning Objective |
| Geometry and measures | Similar shapes (foundation) | Apply the concepts of congruence and similarity, including the relationships between lengths, {areas and volumes} in similar figures. |
| Geometry and measures | Pythagoras | Apply Pythagoras’ Theorem and trigonometric ratios to find angles and lengths in right-angled triangles {and, where possible, general triangles} in two {and three} dimensional figures. |
| Algebra | Proof foundation | Know the difference between an equation and an identity; argue mathematically to show algebraic expressions are equivalent, and use algebra to support and construct arguments {and proofs}. |
| Algebra | Inequalities on a number line | Solve linear inequalities in one {or two} variable{s}, {and quadratic inequalities in one variable}; represent the solution set on a number line, {using set notation and on a graph}. |
| Algebra | Function machines | Where appropriate, interpret simple expressions as functions with inputs and outputs. |
| Algebra | Factorising quadratics a=1 | Simplify and manipulate algebraic expressions (including those involving surds {and algebraic fractions}) by: factorising quadratic expressions of the form x^2 + bx + c, including the difference of two squares; {factorising quadratic expressions of the form ax^2 + bx + c}. |
| Algebra | Expanding double brackets | Simplify and manipulate algebraic expressions (including those involving surds {and algebraic fractions}. |
| Ratio, proportion and rates of change | Density mass volume | Convert between related compound units (speed, rates of pay, prices, density, pressure) in numerical and algebraic contexts. |
| Statistics | Data sampling and questionnaires | Infer properties of populations or distributions from a sample, whilst knowing the limitations of sampling. |
| Geometry and measures | Corresponding angles and alternate angles | Apply and prove the standard circle theorems concerning angles, radii, tangents and chords, and use them to prove related results. |
| Ratio, proportion and rates of change | Conversions | Convert between related compound units (speed, rates of pay, prices, density, pressure) in numerical and algebraic contexts. |
| Geometry and measures | Volume of 3D shapes | Calculate surface areas and volumes of spheres, pyramids, cones and composite solids. |
| Probability | Relative frequency | Apply the property that the probabilities of an exhaustive set of mutually exclusive events sum to one, |
Term 1
| Theme | Topic | Required Learning Objective |
| Number | Surds – rationalise and harder surds | Calculate exactly with fractions, {surds} and multiples of π; {simplify surd expressions involving squares and rationalise denominators. |
| Geometry and measures | Circle theorems | Apply and prove the standard circle theorems concerning angles, radii, tangents and chords, and use them to prove related results. |
| Geometry and measures | Negative enlargements | Interpret and use fractional {and negative} scale factors for enlargements. |
| Statistics | Cumulative frequency | Construct and interpret diagrams for grouped discrete data and continuous data, i.e. histograms with equal and unequal class intervals and cumulative frequency graphs, and know their appropriate use. |
| Geometry and measures | Bearings | Interpret and use bearings. |
| Algebra | Algebraic fractions | Simplify and manipulate algebraic expressions (including those involving surds {and algebraic fractions}). |
| Algebra | Velocity-time graphs | Calculate or estimate gradients of graphs and areas under graphs (including quadratic and other non-linear graphs), and interpret results in cases such as distance-time graphs, velocity-time graphs and graphs in financial contexts. |
| Probability | Stratified sampling | Use a probability model to predict the outcomes of future experiments; understand that empirical unbiased samples tend towards theoretical probability distributions, with increasing sample size. |
| Algebra | Solving simultaneous equations with graphs | Solve two simultaneous equations in two variables (linear/linear {or linear/quadratic}) algebraically; find approximate solutions using a graph. |
| Number | Recurring decimals to fractions | Change recurring decimals into their corresponding fractions and vice versa. |
| Ratio, proportion and rates of change | Ratios higher | Compare lengths, areas and volumes using ratio notation and/or scale factors; make links to similarity (including trigonometric ratios). |
| Algebra | Quadratic sequences | Recognise and use sequences of triangular, square and cube numbers, simple arithmetic progressions, Fibonacci type sequences, quadratic sequences. |
| Algebra | Proof higher | Argue mathematically to show algebraic expressions are equivalent, and use algebra to support and construct arguments {and proofs}. |
| Writing – Vocabulary, Grammar and Punctuation | Reading – Word Reading | Writing – Transcription | Writing – Composition |
| Extend the range of sentences with more than one clause by using a wider range of conjunctions, including when, if, because, although | Apply their growing knowledge of root words, prefixes and suffixes (etymology and morphology) as listed in English Appendix 1, both to read aloud and to understand the meaning of new words they meet | Use further prefixes and suffixes and understand how to add them | Read aloud their own writing, to a group or the whole class, using appropriate intonation and controlling the tone and volume so that the meaning is clear |
| Use the present perfect form of verbs in contrast to the past tense | Read further exception words, noting the unusual correspondences between spelling and sound, and where these occur in the word | Spell further homophones | Plan their writing |
| Choose nouns or pronouns appropriately for clarity and cohesion and to avoid repetition | Reading – Comprehension | Spell words that are often misspelt | Draft and write |
| Use conjunctions, adverbs and prepositions to express time and cause | Listen to and discuss a wide range of fiction, poetry, plays, non-fiction and reference books or textbooks | Place the possessive apostrophe accurately in words with regular plurals and in words with irregular plurals | In non-narrative material, use simple organisational devices |
| Use fronted adverbials | Read books that are structured in different ways and reading for a range of purposes | Use the first two or three letters of a word to check its spelling in a dictionary | evaluate and edit |
| Write from memory simple sentences, dictated by the teacher, that include words and punctuation taught so far |
| Writing – Vocabulary, Grammar and Punctuation | Reading – Word Reading | Writing – Transcription | Writing – Composition |
| Use commas after fronted adverbials | Increase their familiarity with a wide range of books, including fairy stories, myths and legends, and retelling some of these orally | Use further prefixes and suffixes and understand how to add them | Read aloud their own writing, to a group or the whole class, using appropriate intonation and controlling the tone and volume so that the meaning is clear |
| Indicate possession by using the possessive apostrophe with plural nouns | Identifying themes and conventions in a wide range of books | Spell further homophones | Plan their writing |
| Use and punctuate direct speech | Preparing poems and play scripts to read aloud and to perform, showing understanding through intonation, tone, volume and action | Spell words that are often misspelt | Draft and write |
| Use and understand the grammatical terminology in English Appendix 2 accurately and appropriately when discussing their writing and reading | Discuss words and phrases that capture the reader’s interest and imagination | Place the possessive apostrophe accurately in words with regular plurals and in words with irregular plurals | In non-narrative material, use simple organisational devices |
| Recognise some different forms of poetry | Use the first two or three letters of a word to check its spelling in a dictionary | evaluate and edit | |
| Check that the text makes sense to them, discuss their understanding and explain the meaning of words in context | Write from memory simple sentences, dictated by the teacher, that include words and punctuation taught so far | ||
| Ask questions to improve their understanding of a text | |||
| Draw inferences such as inferring characters’ feelings, thoughts and motives from their actions, and justify inferences with evidence | |||
| Predict what might happen from details stated and implied | |||
| Identify main ideas drawn from more than one paragraph and summarise these | |||
| Identify how language, structure, and presentation contribute to meaning | |||
| Retrieve and record information from non-fiction | |||
| Participate in discussion about both books that are read to them and those they can read for themselves, taking turns and listening to what others say |
| Writing – Vocabulary, Grammar and Punctuation | Reading – Comprehension | Writing – Composition |
| Recognise vocabulary and structures that are appropriate for formal speech and writing, including subjunctive forms | Continue to read and discuss an increasingly wide range of fiction, poetry, plays, non-fiction and reference books or textbooks | Plan their writing |
| Use passive verbs to affect the presentation of information in a sentence | Read books that are structured in different ways and read for a range of purposes | Draft and write |
| Use the perfect form of verbs to mark relationships of time and cause | Increase their familiarity with a wide range of books, including myths, legends and traditional stories, modern fiction, fiction from our literary heritage, and books from other cultures and traditions | Evaluate and edit by: |
| Use expanded noun phrases to convey complicated information concisely | Recommend books that they have read to their peers, giving reasons for their choices | Proof-read for spelling and punctuation errors |
| Use modal verbs or adverbs to indicate degrees of possibility | Identify and discuss themes and conventions in and across a wide range of writing | Perform their own compositions, using appropriate intonation, volume, and movement so that meaning is clear |
| Use relative clauses beginning with who, which, where, when, whose, that or with an implied relative pronoun | Make comparisons within and across books | Evaluate and edit by: |
| Learn the grammar for years 5 and 6 in English Appendix 2 | Learn a wider range of poetry by heart | Proof-read for spelling and punctuation errors |
| Use commas to clarify meaning or avoid ambiguity in writing | Prepare poems and plays to read aloud and to perform, show understanding through intonation, tone and volume so that the meaning is clear to an audience | Perform their own compositions, using appropriate intonation, volume, and movement so that meaning is clear |
| Use hyphens to avoid ambiguity | Check that the book makes sense to them, discuss their understanding and explain the meaning of words in context |
| Writing – Vocabulary, Grammar and Punctuation | Reading – Comprehension | Writing – Composition |
| Recognise vocabulary and structures that are appropriate for formal speech and writing, including subjunctive forms | Continue to read and discuss an increasingly wide range of fiction, poetry, plays, non-fiction and reference books or textbooks | Plan their writing |
| Use passive verbs to affect the presentation of information in a sentence | Read books that are structured in different ways and read for a range of purposes | Draft and write |
| Use the perfect form of verbs to mark relationships of time and cause | Increase their familiarity with a wide range of books, including myths, legends and traditional stories, modern fiction, fiction from our literary heritage, and books from other cultures and traditions | Evaluate and edit by: |
| Use expanded noun phrases to convey complicated information concisely | Recommend books that they have read to their peers, giving reasons for their choices | Proof-read for spelling and punctuation errors |
| Use modal verbs or adverbs to indicate degrees of possibility | Identify and discuss themes and conventions in and across a wide range of writing | Perform their own compositions, using appropriate intonation, volume, and movement so that meaning is clear |
| Use relative clauses beginning with who, which, where, when, whose, that or with an implied relative pronoun | Make comparisons within and across books | Evaluate and edit by: |
| Learn the grammar for years 5 and 6 in English Appendix 2 | Learn a wider range of poetry by heart | Proof-read for spelling and punctuation errors |
| Use commas to clarify meaning or avoid ambiguity in writing | Prepare poems and plays to read aloud and to perform, show understanding through intonation, tone and volume so that the meaning is clear to an audience | Perform their own compositions, using appropriate intonation, volume, and movement so that meaning is clear |
| Use hyphens to avoid ambiguity | Check that the book makes sense to them, discuss their understanding and explain the meaning of words in context | |
| Use brackets, dashes or commas to indicate parenthesis | Ask questions to improve their understanding | |
| Use semi-colons, colons or dashes to mark boundaries between independent clauses | Draw inferences such as inferring characters’ feelings, thoughts and motives from their actions, and justify inferences with evidence | |
| Use a colon to introduce a list | Predict what might happen from details stated and implied | |
| Punctuate bullet points consistently | Summarise the main ideas drawn from more than one paragraph, identify key details that support the main ideas | |
| Use and understand the grammatical terminology in English Appendix 2 accurately and appropriately in discussing their writing and reading | Identify how language, structure and presentation contribute to meaning | |
| Discuss and evaluate how authors use language, including figurative language, considering the impact on the reader | ||
| Distinguish between statements of fact and opinion | ||
| Retrieve, record and present information from non-fiction | ||
| Participate in discussions about books that are read to them and those they can read for themselves, build on their own and others’ ideas and challenge views courteously | ||
| Explain and discuss their understanding of what they have read, including through formal presentations and debates, maintaining a focus on the topic and using notes where necessary | ||
| Provide reasoned justifications for their views |
Our KS3 lessons will develop all the main areas of study students need to learn before they enter KS4 (year 10.) We aim to cover a broad selection of texts each term covering Writing fiction, Reading Fiction, Reading Pre-20th Century Fiction, Writing Non-Fiction, Reading 20th Century Play
Our English lessons for KS3 are taught in line with the assessment objectives stipulated in the KS3 national curriculum. The focus of our English classes will include development of reading, writing, grammar/vocab and spoken english.
For more information assessment objectives please visit: https://theacademylearning.co.uk/pdfs/KS3ENGLISHCURRICULUMMAP.pdf
Term 1
- WRITING NON-FICTION (AO’s developed:1b, 1c, 1d, 2a, 2b, 2c)
- READING PRE-20TH CENTURY FICTION (AO’s developed:1ai, 2a, 2b, 3a, 3c)
Term 2
- WRITING FICTION (AO’s developed:2c, 3a, 3e, 1aii, 1c, 1d, 2a 1a
- UNDERSTANDING LANGUAGE CONTEXT (AO’s developed: 1ai; 2a; 2d; 3a; 1aiii; 1aii; 1b; 1d 1c;1f 1a;1b
Term 3
- READING POETRY (AO’s developed: 1aiii, 2b, 2c, 2d, 3a, 3b, 3f 1ai, 1aii, 1b, 1d, 2b, 2c,
- READING SHAKESPEARE (AO’s developed: 1aii, 2a, 2b, 2c, 2d, 3a, 3b, 3c, 3d, 3e 1aii, 1aiii, 1aiv, 1b, 1c, 1d, 2a, 2b, 2c 1e 1a, 1b, 1c, 1d, 1e, 1f
Our KS3 lessons will develop all the main areas of study students need to learn before they enter KS4 (year 10.) We aim to cover a broad selection of texts each term covering Writing fiction, Reading Fiction, Reading Pre-20th Century Fiction, Writing Non-Fiction, Reading 20th Century Play
Our English lessons for KS3 are taught in line with the assessment objectives stipulated in the KS3 national curriculum. The focus of our English classes will include development of reading, writing, grammar/vocab and spoken english.
For more information assessment objectives please visit: https://theacademylearning.co.uk/pdfs/KS3ENGLISHCURRICULUMMAP.pdf
Term 1
- WRITING FICTION (AO’s developed: 2a, 2b, 3a, 3c, 1ai, 1aii, 1c, 1d, 2a, 1b, 1c, 1e, 1f, 1a)
- READING PRE-20TH CENTURY FICTION (AO’s developed: 2a, 2b, 2c, 2d, 3a, 3c, 1aii, 1b, 1c, 1d, 2a, 2b, 1a, 1b, 1e, 1f)
Our KS3 lessons will develop all the main areas of study students need to learn before they enter KS4 (year 10.) We aim to cover a broad selection of texts each term covering Writing fiction, Reading Fiction, Reading Pre-20th Century Fiction, Writing Non-Fiction, Reading 20th Century Play
Our English lessons for KS3 are taught in line with the assessment objectives stipulated in the KS3 national curriculum. The focus of our English classes will include development of reading, writing, grammar/vocab and spoken english.
For more information assessment objectives please visit: https://theacademylearning.co.uk/pdfs/KS3ENGLISHCURRICULUMMAP.pdf
Term 1
- READING POETRY (AO’s developed: 1.a.i; 2.a; 2.b; 2.c; 2.d; 3.a; 3.b; 3.c; 3.d; 3.e 1.a.i; 1.a.ii; 1.b; 1.d; 2.a, 1.d; 1.f, 1.a; 1.b; 1.c; 1.d
- WRITING NON-FICTION (AO’s developed
2.a; 2.b; 2.c; 3.e 1.a.iv; 2.a 1.a; 1.b; 1.c 1.a
Students in year 10 and 11 continue to develop their understanding of all required Assessment Objectives:
- AO1:
- identify and interpret explicit and implicit information and ideas
- select and synthesise evidence from different texts
- AO2: Explain, comment on and analyse how writers use language and structure to achieve effects and influence readers, using relevant subject terminology to support their views
- AO3: Compare writers’ ideas and perspectives, as well as how these are conveyed, across two or more texts
- AO4: Evaluate texts critically and support this with appropriate textual references
- AO5: Communicate clearly, effectively and imaginatively, selecting and adapting tone, style and register for different forms, purposes and audiences. Organise information and ideas, using structural and grammatical features to support coherence and cohesion of texts
- AO6: Candidates must use a range of vocabulary and sentence structures for clarity, purpose and effect, with accurate spelling and punctuation. (This requirement must constitute 20% of the marks for each specification as a whole.)
- AO7: Demonstrate presentation skills in a formal setting
- AO8: Listen and respond appropriately to spoken language, including to questions and feedback on presentations
- AO9: Use spoken Standard English effectively in speeches and presentations.
Please a sample lesson here: https://theacademylearning.co.uk/pdfs/KS4-ENGLISH-SAMPLE.pdf
| Objectives | Success Criteria |
To understand the elements that make up the GCSE English Language exams for AQA (reading element). | • To define the AOs for the paper effectively. • To analyse personal trouble spots within the exams. • To remember the key question types for each paper. |
| To understand the impact and effect of language in a text. | • To revise key language terms. • To analyse the use of language in a text. • To hone and refine analysis of language. |
| To write an exam-style answer to a language analysis question. | • To understand the importance of the reader when considering a text. • To analyse the language used in an exam text. • To express analysis in a clear and coherent way. |
| To be able to explain, comment on and analyse how writers use structure to achieve effects and influence readers, using relevant subject terminology to support their views. | • To distinguish between language and structure. • To track the journey of a text. • To compose and assess sample answers. |
| To be able to explain, comment on and analyse how writers use structure to achieve effects and influence readers, using relevant subject terminology to support their views. | • To distinguish between language and structure. • To track the journey of a text. • To compose and assess sample answers |
| To evaluate texts critically and support this with appropriate textual references. | • To understand how to evaluate a text. • To identify quotations to support your evaluation. • To compose and assess sample answers. |
| To be able to evaluate texts critically and support this with appropriate textual references. | • To understand how to evaluate a text. • To identify quotations to support your evaluation. • To compose and assess sample answers. |
| To identify and interpret explicit/implicit information and ideas, and select and synthesise from different texts. | • To know language of comparison. • To identify quotations from two different texts. • To compose and assess sample answers. |
| To identify and interpret explicit/implicit information and ideas, and select and synthesise from different texts. | • To recap language of comparison • To identify quotations from two different texts • To compose and assess sample answers. |
| To understand the elements that make up the GCSE English Language exams | To review the scope of the intervention sessions so far. • To recap learning through the completion of the quizzes for paper 1 and 2. • To remember the key question types and answer styles for each paper. |
Students in year 11 continue to develop their understanding of all required Assessment Objectives, with an emphasis on exam paper practice before the summer term of each academic year.
- AO1:
- identify and interpret explicit and implicit information and ideas
- select and synthesise evidence from different texts
- AO2: Explain, comment on and analyse how writers use language and structure to achieve effects and influence readers, using relevant subject terminology to support their views
- AO3: Compare writers’ ideas and perspectives, as well as how these are conveyed, across two or more texts
- AO4: Evaluate texts critically and support this with appropriate textual references
- AO5: Communicate clearly, effectively and imaginatively, selecting and adapting tone, style and register for different forms, purposes and audiences. Organise information and ideas, using structural and grammatical features to support coherence and cohesion of texts
- AO6: Candidates must use a range of vocabulary and sentence structures for clarity, purpose and effect, with accurate spelling and punctuation. (This requirement must constitute 20% of the marks for each specification as a whole.)
- AO7: Demonstrate presentation skills in a formal setting
- AO8: Listen and respond appropriately to spoken language, including to questions and feedback on presentations
- AO9: Use spoken Standard English effectively in speeches and presentations.
Please a sample lesson here: https://theacademylearning.co.uk/pdfs/KS4-ENGLISH-SAMPLE.pdf
| Objectives | Success Criteria |
To understand the elements that make up the GCSE English Language exams for AQA (reading element). | • To define the AOs for the paper effectively. • To analyse personal trouble spots within the exams. • To remember the key question types for each paper. |
| To understand the impact and effect of language in a text. | • To revise key language terms. • To analyse the use of language in a text. • To hone and refine analysis of language. |
| To write an exam-style answer to a language analysis question. | • To understand the importance of the reader when considering a text. • To analyse the language used in an exam text. • To express analysis in a clear and coherent way. |
| To be able to explain, comment on and analyse how writers use structure to achieve effects and influence readers, using relevant subject terminology to support their views. | • To distinguish between language and structure. • To track the journey of a text. • To compose and assess sample answers. |
| To be able to explain, comment on and analyse how writers use structure to achieve effects and influence readers, using relevant subject terminology to support their views. | • To distinguish between language and structure. • To track the journey of a text. • To compose and assess sample answers |
| To evaluate texts critically and support this with appropriate textual references. | • To understand how to evaluate a text. • To identify quotations to support your evaluation. • To compose and assess sample answers. |
| To be able to evaluate texts critically and support this with appropriate textual references. | • To understand how to evaluate a text. • To identify quotations to support your evaluation. • To compose and assess sample answers. |
| To identify and interpret explicit/implicit information and ideas, and select and synthesise from different texts. | • To know language of comparison. • To identify quotations from two different texts. • To compose and assess sample answers. |
| To identify and interpret explicit/implicit information and ideas, and select and synthesise from different texts. | • To recap language of comparison • To identify quotations from two different texts • To compose and assess sample answers. |
| To understand the elements that make up the GCSE English Language exams | To review the scope of the intervention sessions so far. • To recap learning through the completion of the quizzes for paper 1 and 2. • To remember the key question types and answer styles for each paper. |
Topics covered from September – August
- Living things and their habitats
- Earth and space
- Forces
- Properties of materials
- Animals including humans
- Scientists and inventors
Topics covered from September – August
- Animals including humans
- Light
- Evolution and inheritance
- Electricity
- Living things and their habitats
- Scientist and inventors
Topics covered from September – August
- Cells and organisation
- Ecosystems and interdependence
- Health and the human body
- Inheritance and evolution
- Photosynthesis and respiration
- Reproduction
Topics covered from September – August (students will develop their understanding in all the key area below, building on their knowledge of these topics from year 7)
- Cells and organisation
- Ecosystems and interdependence
- Health and the human body
- Inheritance and evolution
- Photosynthesis and respiration
- Reproduction
Topics covered from September – August (students will develop their understanding in all the key area below, building on their knowledge of these topics from year 8)
- Cells and organisation
- Ecosystems and interdependence
- Health and the human body
- Inheritance and evolution
- Photosynthesis and respiration
- Reproduction
(*) Indicates topics covered as part of the triple award.
September: Cell biology |
Eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells Specialised Cells |
Microscope and Magnification 1 Microscope and Magnification 2 Chromosomes and Mitosis Stem Cells |
October: Organisation |
The Circulatory System Health and risk factors |
An Introduction to Enzymes Enzymes in the digestive system |
November : Infection and response |
Preventing the spread of pathogens |
Viral, bacterial, fungal and protist diseases Immunity and vaccination |
December: Bioenergetics |
Photosynthesis |
The rate of photosynthesis – Limiting Factors Investigating the rate of photosynthesis Respiration and metabolism |
The effect of exercise on the body |
January: Homeostasis and response |
The nervous system |
Hormones in human reproduction |
Adrenalin and Thyroxine Controlling blood glucose |
February/March: Inheritance, variation and evolution |
Genetic inheritance |
Asexual vs sexual reproduction and meiosis DNA and the genome |
Natural Selection |
April: Ecology |
Adaptation |
Human impact on the environment |
Communities and interdependence Cycling in ecosystems |
May: Revision
June: Revision
July-August: Mixed topics
(*) Indicates topics covered as part of the triple award.
September: Cell biology |
Diffusion Osmosis |
Active Transport |
*Culturing Microorganisms |
October: Organisation |
Cardiovascular disease Transpiration in plants Organisation in plants |
November : Infection and response |
Fighting diseases with drugs |
*Monoclonal antibodies |
*Plant diseases and defence responses |
December: Bioenergetics |
Photosynthesis |
The rate of photosynthesis – Limiting Factors Investigating the rate of photosynthesis Respiration and metabolism |
The effect of exercise on the body |
January: Homeostasis and response |
*The brain & The eye |
*Controlling body temperature Maintaining water and nitrogen balance Plant hormones: Coordination and use |
February/March: Inheritance, variation and evolution |
Inherited disorders – Polydactyly Inherited disorders – Cystic Fibrosis Screening for genetic disorders Selective breeding |
Genetic engineering |
Evidence of evolution and extinction Classification and evolutionary trees |
*Reproducing both ways |
*DNA structure and protein synthesis Cloning |
*Theories of evolution and speciation The History of genetics |
April: Ecology |
Rates of decomposition |
Measuring the Distribution of Organisms |
*Impact of environmental change Trophic levels in an ecosystem Sustainable food production |
May: Revision
June: Revision
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
We think it’s a much better idea to allow students to meet our tutors and get a feel of how our classes run. So instead of an initial assessment, we offer a free 1-1 trial lesson where your child will get a chance to immerse themselves into one of our weekly classes. Following the trial lesson, our tutors will provide constructive feedback which we’ll use to ascertain which course and level will be best suited for your child.
We’ve run our tuition programmes since 2007 and over the years we’ve developed a deep understanding of how to get each and every child to achieve the best they can. We use a combination of monthly Student Progress Reports, Weekly Quick Tests, Workshops and End of Theme exams to ensure all our students are working towards their target grades. During your enrolment, we’ll ask you for your most recent school report which we’ll also use to monitor progress.
Following your trial lesson with us, we will assign your child with their classes. These classes will be held on a fixed time and day every week of the term, so that you’ve got a clear schedule to plan your week. Classes are held on a weekday evening from 4.30pm onwards as well as on the weekend between 9am and 6pm. We will assign your child to a group based on where we think their learning will be best supported.
We use a combination of a virtual whiteboard and Google Class to hold all our online lessons.
Sure we can! Although we run an intensive programme, we’ll always make time to help students with concerns they have with school homework. We won’t complete school homework for anyone, or help fill out answers, but we will steer students in the right direction through teaching and worked examples.
Homework is given in all our classes every week and is there to support students through ideas and principle covered during our lessons. Whilst we encourage homework to be completed every week, we understand that this may not always be possible. If your child is unable to complete homework, please let our tutors know. This way any additional support that maybe required in class can be provided. Ofcourse, students will be required to catch up on missed homework as soon as possible!
We teach in small groups based on ability so that each student can benefit from one-on-one time with the teacher and get the individualised support they need. Although the maximum capacity of our classes is 12 students, there are usually no more than 5-7 students per teacher for advanced students, whilst groups requiring more support will usually be 3-5 students large. Our aim is always to keep class size as small as possible!
Our teachers will have at the minimum a Qualified Teacher Status (QTS), a relevant degree or be working towards a degree that is at least 2.1 or higher and relevant to the subject they teach. They will also have specialist knowledge in their given subject areas, extensive experience of working with children in an educational setting and a sound knowledge of the national curriculum. Most importantly, all our teachers undergo a rigorous training period under our management team, departmental heads and Mr Vora who founded the schools. On-going training is also provided to ensure all teaching staff are providing the best level of care to our students.
We firmly believe that teachers who have attained the best grades through their own learning at school will be the most valuable asset to our students. Our group of high-flying teachers, are able to impart their own experiences in their teaching in order to ensure the very best results. All of our tutors will have attended a UK top 10 university, including Oxbridge and The Russell Group Institutions.
All teachers at The Academy hold a clear DBS disclosure certificate.
Although this is a rarity, there may be times when a tutor is unable to teach your child. We have a number of provisions in place. Our departmental structure, means that there is usually always another subject specialist who will be able to teach. In some cases, we may reschedule this class later in the term (either online or at our study centre.) Parents will never be charged for any classes that have not taken place.
We teach students from KS2 right the way through to KS5 (A-Levels.) Our A-level teaching sessions are held in small groups of 1-4 students and we’re able to offer all subject choices. Get in touch with us to find out more.
find out more
If you would like to come along and have an initial consultation with one of our teachers to decide what your child’s needs are, then please get in touch by filling in the form.
